This site uses cookies to provide you with a great user experience. By using BondbloX, you accept our use of cookies.
Bond Market News
Lebanon Upgraded to CCC as Fiscal Surplus and Reforms Aid Debt Service
August 18, 2025
Lebanon was upgraded to CCC by S&P on Friday, citing modest improvements in the government’s capacity to service local currency commercial debt. The upgrade is supported by recurring fiscal surpluses since 2023, progress on key reforms, and a reduced stock of local currency debt. The Lebanese pound has depreciated by about 98% from 2019-24. Combined with elevated inflation, this resulted in the value of local currency debt falling to 2% of GDP (<$1bn) at end-2024 vs. 100% of GDP before 2020.
The government defaulted on Eurobonds in 2020 and stopped interest payments on local debt to the central bank from 2021 to 2023. However, they have resumed coupon payments from 2024 and plan to clear previous arrears starting this year. Lebanon’s GDP has halved from $55bn in 2018 to $28bn in 2024. However, S&P expects the trend to reverse and the GDP to gradually expand by 2.3% in 2025-26. S&P also projects Lebanon’s debt-to-GDP ratio to fall to 113% in 2025 from 240% in 2022, aided by the currency stabilization, high nominal GDP, and fiscal control.
The new government, formed in early 2025, has moved forward with key reforms including the Bank Restructuring Law and amendments to banking secrecy, both preconditions for an IMF program. However, the crucial Financial Gap Law is still pending and delaying broader debt restructuring, says S&P.
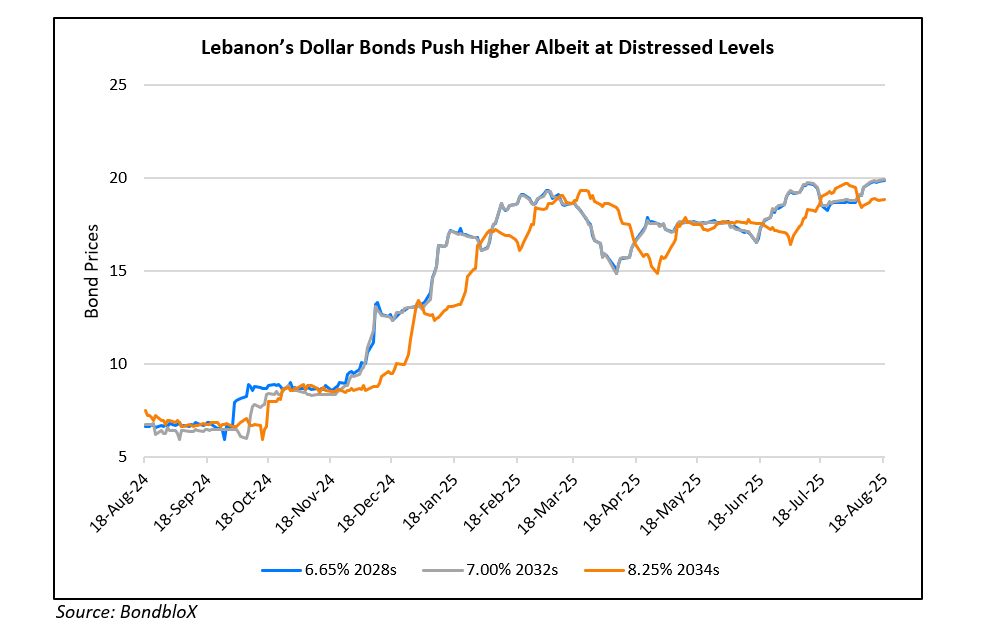
Lebanon dollar bonds have recovered sharply (~4x) from their all-time lows in 2024, albeit still at distressed levels of ~20 cents on the dollar, as seen in the chart above
For more details, click here..
Go back to Latest bond Market News
Related Posts: